31
thewater temperatureaverageswhile
stillprovidingasafety factor for
droughtsandhigher inlet temperatures
during thesummermonths.
W3LiquidCoolingClass:
By reviewing
thesample riverwater temperature
maximums itcanbeseen that thewater
temperaturesexceed the limits fora
W3 liquidcoolingclass, butonly for
shortperiodsof theyear.Becauseof
this, anysystem thathada requirement
tomeet theW3classwouldstill need to
havea fullysizedcooling tower system
tocover thedurationsofhigh
temperature. Insteadof thissystem
design, itmaybemorebeneficial to
providechillers thatcouldprovide
colderwater to thedatacenter
distributionsystem. The riverwater
would instead replacecooling towers
as themaincoolingmeans,withchiller
sized toprovidecolderwaterwhen
necessary.
Asshown inFigure5, cooling towers
are replacedwith the lakeor river
source, butachillerwithaparallel heat
exchanger remains toensure that the
distributionwatercanbeaconsistent
temperature.
W4LiquidCoolingClass:
TheW4class
reliesoncooling towersordrycoolers
as themaincoolingequipment. Since
the facilitysupplywater temperature is
muchhigher, it ispossible tooperate
without theneed formechanical
equipmentwhenusingonly the lakeor
river sourcecooling.
W5LiquidCoolingClass:
The last liquid
coolingclasshas thehighest
temperature rangewith the
expectation thatheat from thedata
centerwouldsupport thebuilding
heatingsystem. In thisscenario, a lake
or rivercoolingsourcecouldprovide
heat rejectionsimilar to theW4class,
butassupplemental afterproviding the
neededenergy to thebuildingheating
system.
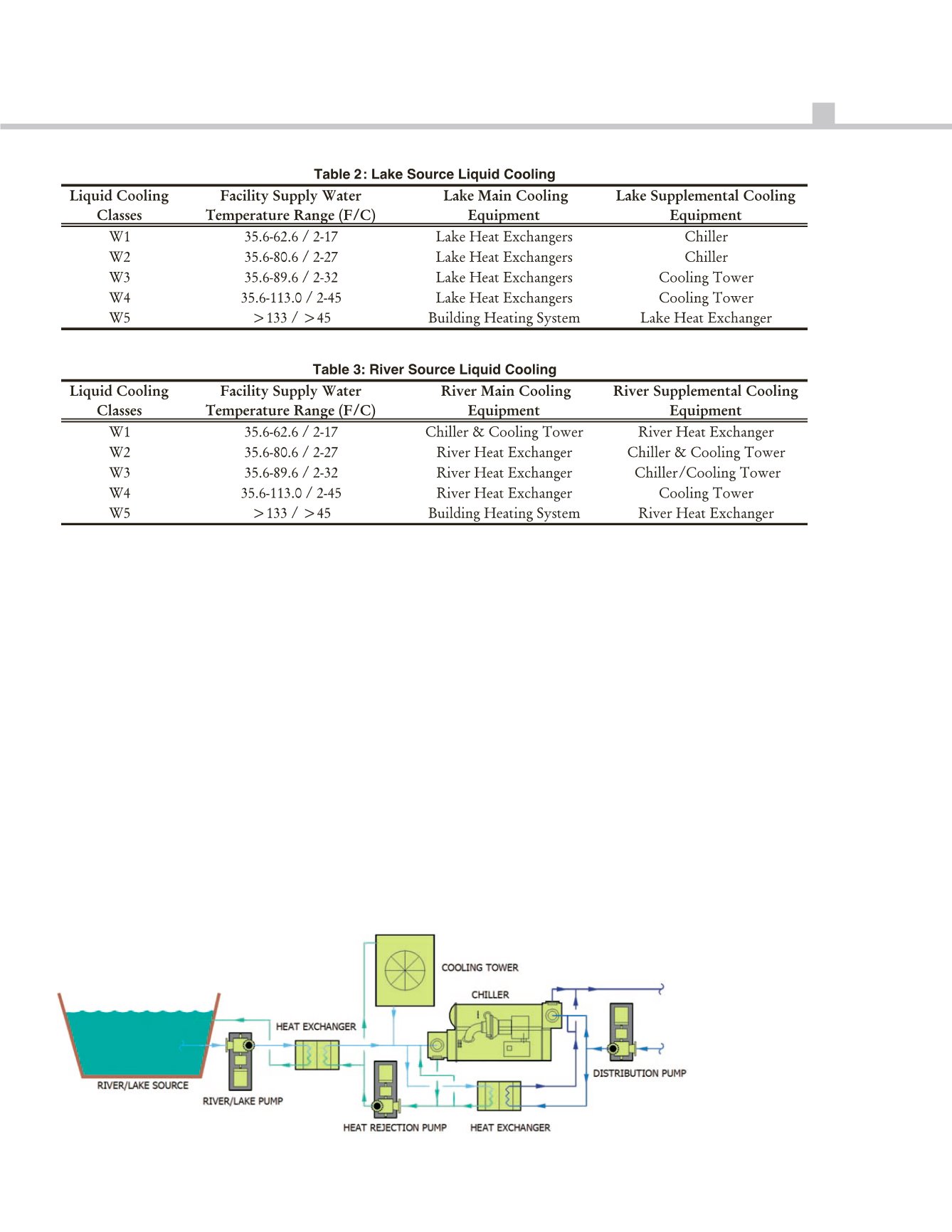
ThesystemdescriptionsonTables2
and3, below, showproposed
substitutionsof themainand
supplemental coolingequipment for
lakeand river sourcecooling,
respectively.
LiquidCoolingClassEquipment
SchematicDiagrams
Toassistwithpotential system
configurations, the following
schematicsshowhoweachof the liquid
coolingclassescanbesupported
dependingon the requiredsupply
water temperature.
Figure5presentsanoptionwitha
chillerplant thatcanbesized to
support 100%of the required loador
lessdependingon the liquidcooling
classor
redundancy
required. This
system
configuration
couldsupport the
W1,W2andW3
liquidcooling
classes,with
river/lakewater
providinga
greater
opportunity for
economicsavings
as the facility
supplywater
temperature
increases.
Figure5:Chillerplantwith river/lake source cooling


